Beginner’s Guide: User Role Management in WordPress
WordPress is a CMS that comes with its own user role management system. This user role management in WordPress defines what access does a specific user has, what the user can do and cannot do on the website. As your website grows, it is important to know these user roles and permissions.
One really important thing to understand before starting is that user roles should be assigned keeping in mind what user will be doing on the site.
Do you want to allow user to generate their own content and publish on your WordPress site? Which user should have how much permissions? All these questions will help in improving security of your WordPress website through user role management.
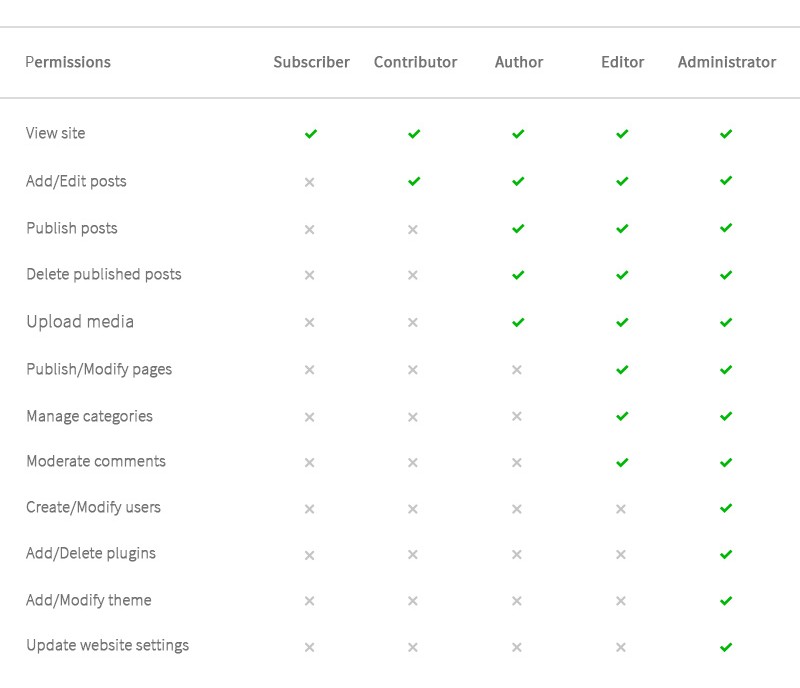
Below is a table which explains the user roles in brief
By default, there are 5 different user roles in WordPress. Each having its own permissions.
- Subscriber – Basic account, assigned to visitor who signs up on the website. Can only read or visit site.
- Contributor – Can edit and delete posts, but can’t publish them. Not allowed to upload media
- Author – Allowed to publish posts, upload media, approve comments. Don’t have access to website settings or publish pages.
- Editor – Does have access to some website settings and can manage user roles and settings of lesser authoritative roles. Can publish pages and edit them. Can’t add plugins or change theme or other website settings
- Administrator – Highest level of account with every permission to access website content or edit it. The default username is admin. For security purposes it is recommended to change the default admin user.
Let’s get into details of user role management in WordPress
Subscriber
A subscriber role has the least website permissions. All this user role can do is login to your WordPress site and edit or update their user profiles. Within their profiles, they can only change their passwords. This user cannot create or edit posts or does not have access to the WordPress site’s dashboard.
Generally, this user role is beneficial when you require someone to login first to view posts or comments.
Contributor
Contributors are users who can create and edit their own posts. They can add tags to their posts. However, they cannot publish posts and select categories of a post.
This role doesn’t have permissions to add media to their own posts, which is sort of a disadvantage as an editor or admin has to work on the post after it is submitted for review.
Contributors can view comments on their posts, they can reply to a comment but cannot approve or disapprove a comment delete a comment.
They also don’t have access to website settings like plugins or themes, hence cannot change any settings on the site.
Author
As briefed earlier, an author can write, edit and publish posts. This user can also delete their own posts in case they are published.
Unlike contributors, who cannot upload media to the posts, an author can do upload media files to posts. Also they can select categories, an author can select categories for post, but these categories have to be added beforehand by an editor or an admin.
Authors can view comments on their posts, they can reply to a comment but cannot approve or disapprove a comment or delete a comment.
This user doesn’t have access to website settings like plugins or themes, hence cannot change any settings, making it a low-risk user, but has the ability to publish or delete their own posts.
Editor
The user role management in WordPress has provided us with an editor role. This is the second highest role in terms of permissions and has almost full content control on the site. This user can create, edit, publish or delete any WordPress posts or pages. An editor can also monitor/moderate comments.
An editor can manage post categories. It can add, edit or delete categories of posts.
An editor however, doesn’t have access to add or delete plugins or themes on the site. It also cannot add new users or manage them.
Administrator
Lastly, the Administrator. This user role is the godfather of all roles. It is the most powerful user role of WordPress, hence should be given to someone carefully if you have to.
Users with their role set as Administrator have access to everything on your WordPress website. This user actually looks after the user role management in WordPress.
This role is basically for website owners and gives full authority over content and website settings. Apart from all the permissions of an editor has, an administrator can add or delete plugins, change between themes and most importantly, add new users roles, even an administrator.
They can also change password of users or even delete users including user roles as administrator.
Must read for Administrators: How to change default Admin user and user id in WordPress?
So, this was all about the what are the user roles and their responsibilities. Now, let’s get into how to assign/modify user roles.
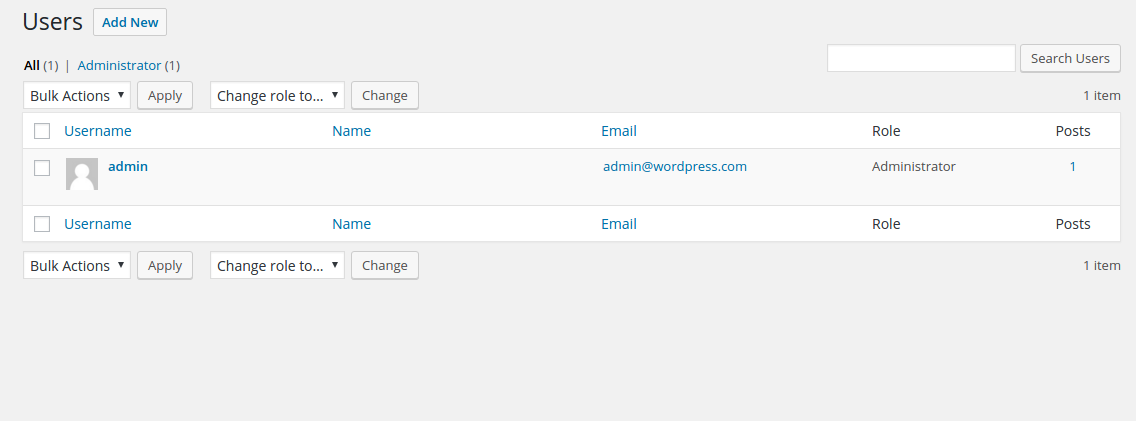
First of all, to assign or modify user roles you need to have an administrator account. Once you login through your admin account you will see the Dashboard or your WordPress site. Under this you need to go to the Users tab.
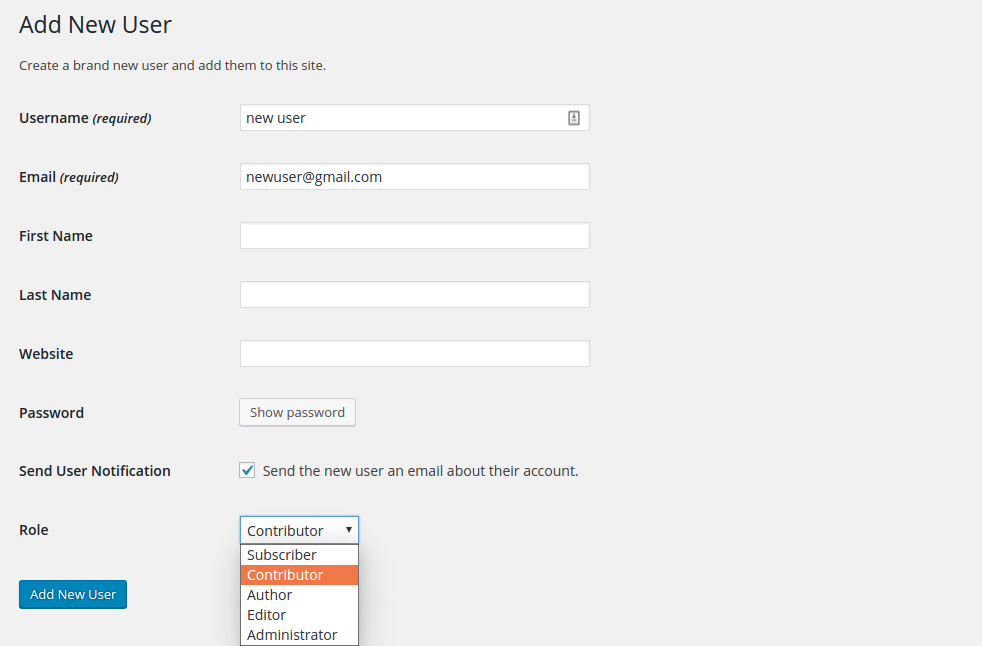
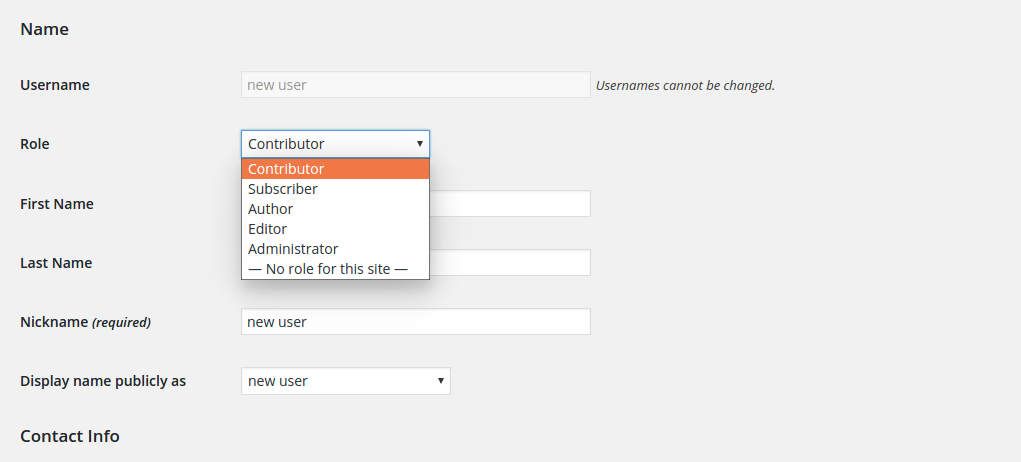
In order to create a new user, you need to click on the ‘Add New’ button. This will give you the following screen. Fill in the necessary details with ‘required’ written in brackets.
Here you can see, that you can select the role from the drop down. Set the required role and click on ‘Add New User’ button. The user will now be added in your user list.
Now if you want to modify a user role, you need to search it in the user list and edit the user. Select whichever role you would like to assign to the user and ‘Save Changes’.
This will update the user’s role for your WordPress site.
Manage user roles in WordPress with plugins
As you can see, by default WordPress doesn’t offer many options in regards to user roles and its management. So, in this section you will learn about a few WordPress plugins that efficiently manage user roles and give some more options or capabilities in customizing it.
This is one of the most popular user management plugin. It gives you ability to manage various user roles and its capabilities on your site. Once you’ve this plugin on your WordPress site, you’ll see a link titled ‘Capabilities’. Here you can customize the permissions of any user or even add new user role. Such plugins ensure proper user role management in WordPress.
2. Members
Apart from having all the functionalities of editing, deleting or adding new user roles or permissions, this WordPress user management plugin has a few other features up its sleeves.
With this plugin, you can restrict any user from viewing your website content. You can create shortcodes to deny access to certain pages or insert a login form or you can even make your site private to all.
Advanced Access Manager is a plugin that allows you to manage user roles and their permissions in WordPress. It allows you to create, edit, delete or manage user capabilities. This plugin can track each user’s activity and can define number of login attempts to your site.
WPFront User Role Editor is a simple plugin which not many features, but it does get your job done. It is very simple to navigate through this plugin and you can change the default user role of user on registration.
Conclusion
User role management in WordPress is a boon from every website owner. It ensures easy management of users on your WordPress site and improved security.





Hello Ravi, Thank you for showing us the crucial role of a user in the management of WordPress. The different role of the user and the permission related to it depends on the use of the user. For instance, if the user wants the hold on upload of media, comments and post then the role of author suits best for him.
Hi Sam,
That’s right. User roles in WordPress are actually designed very intelligently. Kudos to WP.